by Sar Ahmed, MD
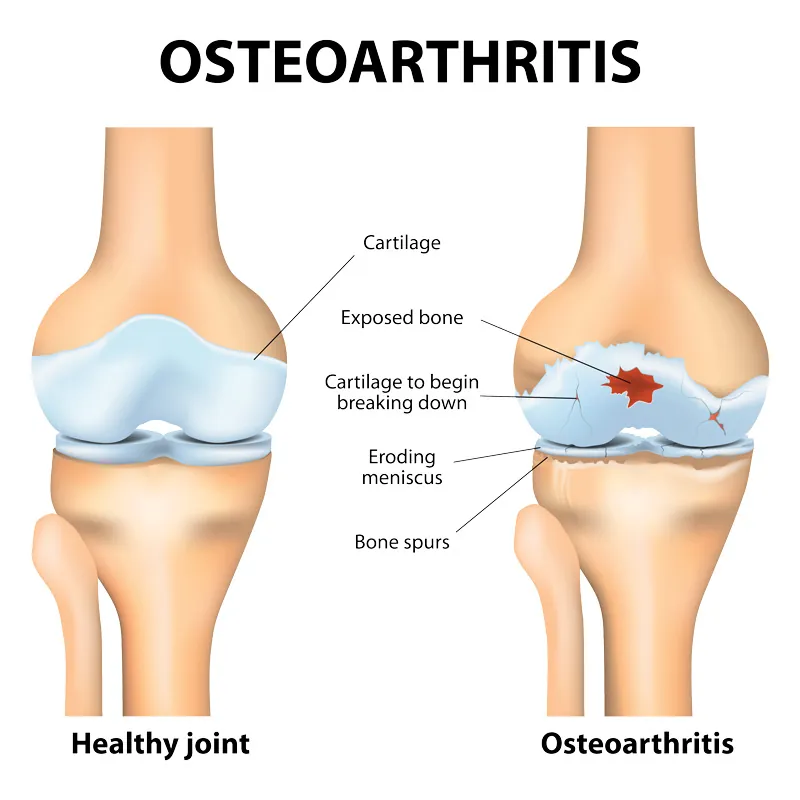 Did you know that osteoarthritis is one of the most frequent causes of disability among adults in the US?
Did you know that osteoarthritis is one of the most frequent causes of disability among adults in the US?
Arthritis is the leading indication for joint replacement surgery. Patients who require surgical treatment for osteoarthritis of the hip have developed the condition naturally over time due to various risk factors; or, in an accelerated fashion, due to prior trauma, injuries, or infection. With rising life expectancy, it is estimated that the prevalence of hip osteoarthritis will continue to increase. The number of people older than age 65 is expected to increase from 37.1 million to 77.2 million by 2040.
4 factors that increase the risk for developing osteoarthritis of the hip include joint degeneration due to:
- Genetics
- The shape of the bones/joint
- Obesity
- Past trauma
The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS) has the best clinical practice guidelines on current evidence-based medicine. This information helps the patient and physician achieve optimal outcomes managing arthritis without surgery and joint replacements.
Below are four nonsurgical treatment options for hip arthritis.
- Physical therapy – Strong evidence supports the use of physical therapy as a treatment to improve function and reduce pain for patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and mild to moderate symptoms. Although there is no real support for pre-surgery PT to improve early function before total hip replacement.
- Non-narcotic management – Strong evidence supports NSAIDs improving short-term pain, function, or both.
- Glucosamine sulfate – Moderate strength evidence does not support the use of glucosamine sulfate because it did not perform better than placebo for improving function, reducing stiffness, and decreasing pain for patients.
- Joint injections – Strong evidence supports joint steroid injections to improve function and reduce pain in the short term. However, strong evidence does not support joint injection with hyaluronic acid.
Many factors can help to reduce the complications from hip replacement before the surgery; here are the most common:
- Obesity – Moderate strength evidence supports that obese patients do not achieve the same level of function after a hip replacement but maybe just as satisfied as patients without obesity. There is limited evidence supporting an increased risk of dislocation, superficial wound infection, and blood loss after total hip arthroplasty.
- Age – There is moderate evidence that older age is associated with lower functional and quality of life outcomes in patients with symptomatic hip osteoarthritis undergoing total hip arthroplasty. There is also limited evidence that older age may be associated with a higher mortality risk with total hip replacement. Finally, there is also some evidence that younger patients may have a higher risk of revision surgery.
- Mental health – Another critical factor to consider is mental health. There is moderate evidence that disorders such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis, are associated with decreased function, pain relief, and quality of life outcomes with total hip replacement.
- Tobacco use – There is some evidence that patients who use tobacco products are at an increased risk for complications after total hip arthroplasty.
Some questions might arise for the actual surgical procedure, such as the type of anesthesia, the approach used for the total hip replacement, and physical therapy.
- Anesthesia – Total hip replacement is typically done under general or spinal anesthesia. Deciding between different types of anesthesia is based on multiple factors, such as medical history or patient/surgeon/anesthesiologist preference. This would be discussed with the surgeon/anesthesiologist to make the best decision for your surgery.
- Surgical Approach – Although there are several approaches to total hip replacement surgery, your surgeon can discuss the best option for you based on your anatomy, the severity of your arthritis, your specific implant, and previously had hip surgery.
- Physical therapy –Prehabilitation physical therapy and Postoperative physical therapy can be very beneficial to improve early function and return to activity.
Dr. Ahmed is an expert orthopedic surgeon who specializes in treating various orthopedic conditions. If you wish to be advised on the most appropriate treatment, please call (877) 821-4657 to schedule an appointment or request an appointment online.
If you are seeking or are scheduled for a surgical hip procedure, don’t wait to seek a pre-and post-physical therapy consultation. Contact a Foothills physical therapist for a free injury assessment.
About Dr. Ahmed
Dr. Ahmed received his Bachelor of Science degree from the University of Buffalo, where he graduated summa cum laude through the advanced honors program. He was inducted into the Phi Beta Kappa, Omicron Chapter, and the Golden Key National Honor Society. Dr. Ahmed completed his medical degree, General surgery internship, and Orthopedic residency through SUNY Upstate Medical University at Syracuse.