by Ashley Stratton PT, DPT, OCS
East Scottsdale
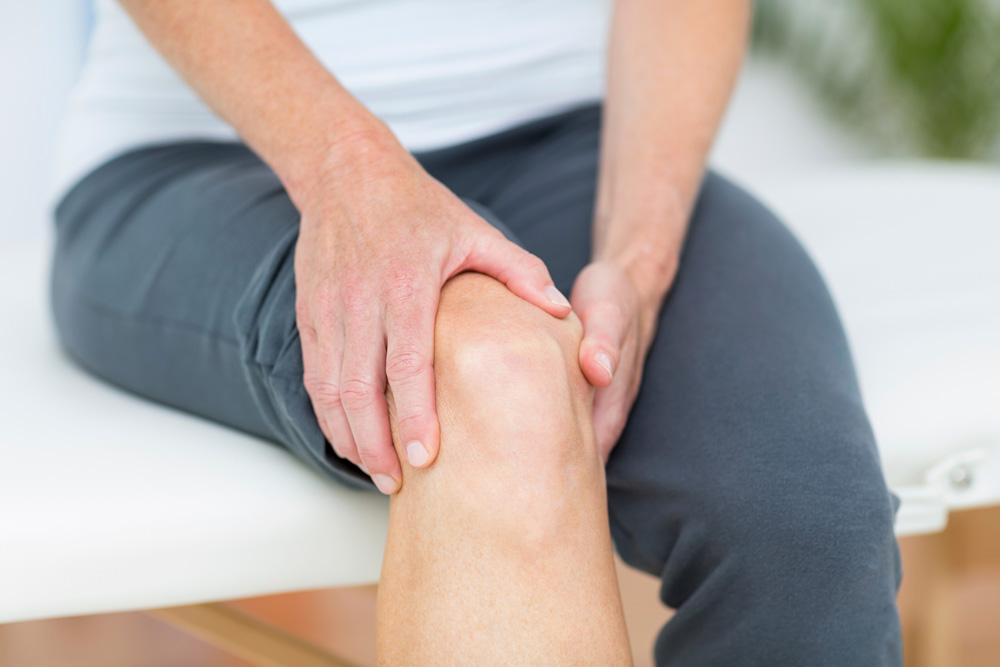
Knee pain is the most common musculoskeletal complaint requiring medical care, as one-third of all patients who visit a doctor for pain involve the knee and muscles surrounding it.
While athletes and people who perform physical work may be at greater risk for knee pain, it can affect anyone at any age. There are many different causes of knee pain, and though some require surgery to resolve, others respond to conservative treatment measures such as physical therapy.
Here are some possible causes, treatment options for knee pain, and prevention tips.
Why Is the Knee a Common Source of Musculoskeletal Pain?
The knee is one of the most significant weight-bearing joints in the body. It works hard to keep you upright when you are standing or walking. For this reason, it is subject to tremendous pressure. Over time, the constant wear and tear on the knee joints can cause chronic pain.
The knee is also a common site for acute pain, i.e., severe discomfort that comes on suddenly. This can occur due to a traumatic impact, such as a car accident. Acute knee pain can also occur when the knee gets twisted in a way that it is not supposed to go, which is common during sports or physical activity but can also occur due to a slip and fall.
What Are Some Common Causes of Knee Pain?
There are many possible causes of knee pain, including injuries and underlying medical conditions. Some are more common than others.
1. Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation of a joint. In the knee, this can occur due to damage to the cartilage that provides cushioning to the joint. The knee bones then have decreased joint protection, causing friction that results in joint pain and swelling.
Two different types of arthritis are most likely to cause knee pain. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its cartilage, causing it to break down. When the cartilage in the knee wears down over time, the degenerative process is known as osteoarthritis.
2. Tendonitis
Tendons are strong bands of fibrous tissue that connect muscles to bones. They help joints to move from the muscles that act on them properly. Tendonitis occurs when these tissues become inflamed, usually due to muscle overuse or joint impairment.
3. Ligament Sprains
Ligaments are connective bands of tissue similar to tendons, except that they connect from bone to bone. They allow joint movement while limiting the range of motion and help provide joint stability. Trauma to the knee can cause the ligament to stretch or tear.
An injury to a ligament is called a sprain. In addition to an inflammatory response of pain and swelling, a sprain can cause knee instability.
3. Cartilage Tears
A meniscus is a crescent-shaped structure in the knee made of cartilage that helps to enhance the knee’s stability while working as a shock absorber. Each knee has two menisci, and meniscus tears frequently occur due to traumatic impact or twisting.
What Are Some Treatment Options for Knee Pain?
Treatment options for knee pain depend on what is causing it and whether it is acute or chronic. A treatment course often begins with self-care to get the symptoms under control, consisting of the following steps:
- Icing the knee to relieve pain and reduce swelling
- Rest to allow the inflammation to subside
- Support, e.g., knee braces, straps, or taping, to reduce pain and swelling and protect the knee from further injury
If your injury is relatively mild, these steps may be sufficient to resolve your knee pain completely. However, if the pain persists or interferes with walking or other activities, you should seek medical treatment.
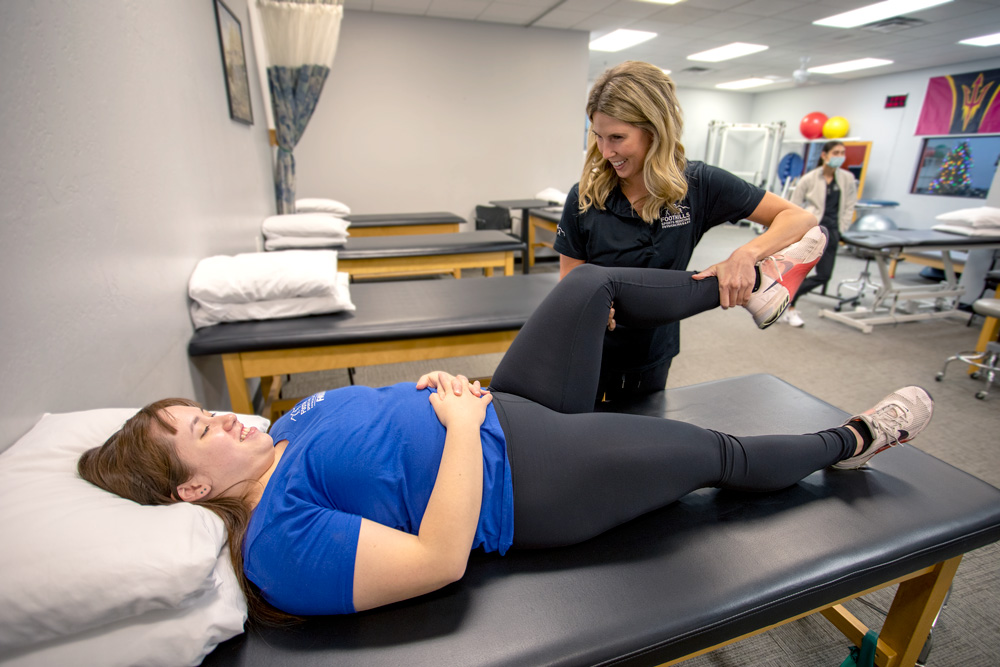
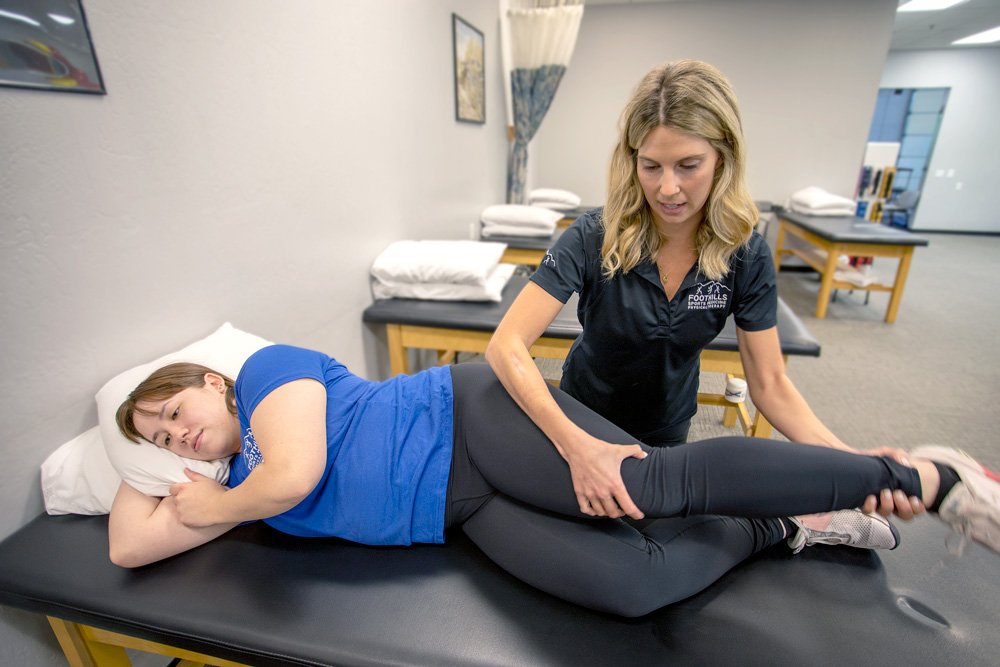
Physical therapy is often key to treating knee pain. Physical therapy exercises help relieve pain and increase the knee’s stability by strengthening the muscles around it. The exercises also help to improve your balance and flexibility, all of which can help you avoid future injuries.
Physical therapy can be used to treat both acute and chronic knee pain. Other possible treatments for chronic knee pain include injections to reduce inflammation and cushion the joint. Acute or chronic knee pain that does not respond to other treatments may require surgery to resolve.
How Can You Prevent Knee Pain?
Because of the many factors that can contribute to it, it is not always possible to prevent knee pain. However, there are things you can do to decrease your risk of developing it.
One of the most important things you can do to prevent knee pain is to stay physically active. This helps to keep your muscles strong for better stability and also helps to keep your weight down to avoid unnecessary strain on your joints.
High-impact activities can put pressure on your joints and contribute to your pain, so you may want to limit these activities or discontinue them altogether. Cycling and swimming are low-impact activities you can do to give your knees a break while getting the exercise you need.
Before exercising, you should stretch out your legs to warm up your muscles. When exercising outside, stick to paved surfaces that are smooth and in good repair. Roads or walkways that are pocketed or rough may put extra pressure on your knees and put you at risk for a fall.
Footwear that does not provide sufficient support can contribute to knee pain. Replace the shoes you use for exercising frequently. Choose shoes with adequate arch support or use orthopedic inserts if needed.
If you are suffering from knee, ankle, or foot pain, schedule an appointment at any of our valley-wide locations. No referral is required. We accept all major insurance carriers and participate with many local provider networks.