Pain in the buttocks may originate from the sacroiliac joint (SI joint). The sacrum is the bony structure below your lower vertebrae and above your tailbone. The ilium is the top part of the pelvis. There are two SI joints in the human body where the two ilia connect to the sacrum. The SI joints are held in place by strong ligaments.
Problems with the SI joint can cause pain that can affect the groin, thighs, low back, and more. A physical therapist may perform testing of the SI joint to assess its positioning and determine whether it is a source of the pain.
What Conditions Can Cause SI Joint Pain?
Sacroiliac pain occurs because of inflammation of the SI joint. This can occur for several different reasons:
- Arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Ligament damage
- Repetitive stress from high-impact activity (e.g., jogging)
- Traumatic injury
Sacroiliac pain can also occur during pregnancy due to hormones released to prepare the body for childbirth.
Chris Adam is an Arizona-based physical therapist with certifications in dry needling and personal training. He explains that the debate among physical therapists around the SI joint as a source of pain is because of the “wide variety of uncontrolled variables which can influence or mimic pain in this area. The amount of motion available, prevalence of SIJ joint dysfunction, and the classification of the joint are all questions which have not been answered with high quality research to date.”
What Is the Difference Between SIJ Testing and SI Joint Provocation Tests?
There are a wide variety of general SIJ tests that, in Adam’s words, are intended to “assess static and dynamic anatomical positioning of the pelvis and sacroiliac joints.” In other words, SIJ tests are performed to determine whether the hip, particularly the SI joint, is in the correct anatomic position when standing or moving.
SI joint provocation tests are a particular type of test designed to reproduce the pain that the patient is experiencing. If the tests are negative, it rules out the SI as a pain generator. According to Adam, “A positive provocation test essentially means that the SIJ joint is likely involved in the patient’s pain experience,” although it may not be the primary source.
When and How Should a Physical Therapist Perform These Tests?
During a physical therapy evaluation, the therapist should first perform a comprehensive exam to gain a general understanding of the patient’s endurance, flexibility, joint mobility, and strength. Only then should special tests be performed to “rule in specific impairments,” according to Adam.
Adam goes on to state that SI joint provocation tests should not be performed in a vacuum. Instead, “It is also important to perform special tests of neighboring joints to rule out other possible diagnoses contributing to the patient’s SIJ pain.” These may include femoroacetabular osteoarthritis, hip impingement, and lumbar spine facet joint dysfunction.
What Are Some Common SI Joint Provocation Tests?
If you are a patient seeing a physical therapist for pain in the low back or buttocks, here are some of the SI joint provocation tests he or she is most likely to perform:
- Sacral Thrust Test: The therapist applies anterior pressure to the sacrum with his or her hands while you lie facedown on the examining table
- Compression Test: The therapist stands behind you while you lie on your side and spreads the SI joint apart by applying downward pressure through the anterior ilium.
- Distraction Test: The therapist applies pressure to the outside of the hips to spread the anterior superior iliac spines on each side. This test is performed as you lie on your back.
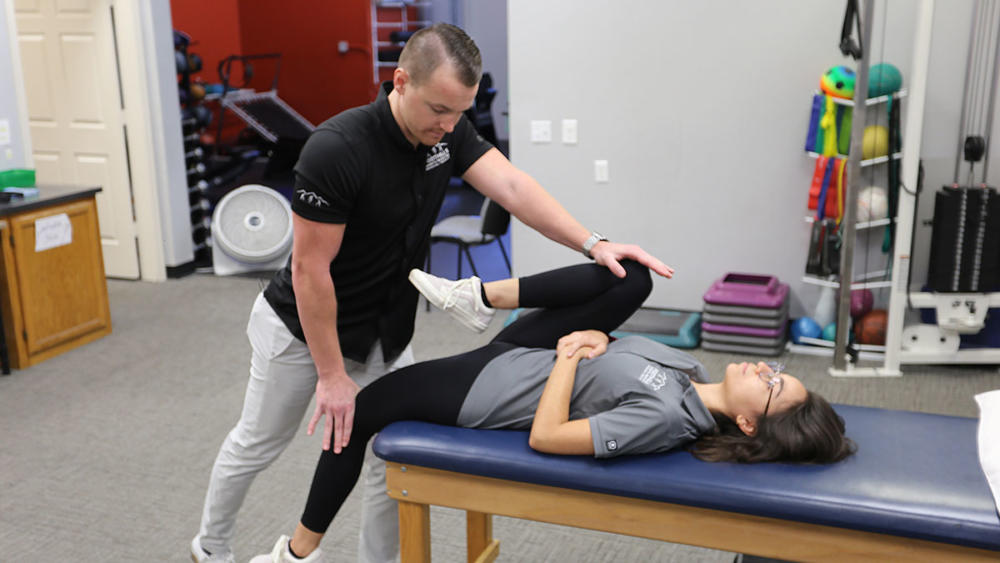
- Gaenslen’s Test: During this test, you lie near the side of the examination table on your back. The therapist stands by your side and places the leg closest to him or her off the table. You will bring the other leg to your chest and hold it there while the therapist puts pressure on the leg that is off the table to cause the hip to extend. The same test may then be performed on the opposite side.
These tests have high diagnostic accuracy for identifying the SI joint as the source of your pain. In fact, compared to special tests for other parts of the body, SI joint provocation tests have the highest diagnostic accuracy. This can be increased even further by performing special tests together in a cluster.